Overview (Unit 4.1)
Alan Turing raised the idea of Universality and considered the theoretical model.
This idea was turned into practice by Von Neumann, who built the first serious architecture of a general computing machine.
How the Instructions look in a computer
0100010 0011 0010
ADD R3 R2 : Add R3 to R2
Memory Hierarchy
Accessing memory directly could be costly, because the addresses are long, and getting a value from a large bulk of memory is very slow compared to the CPU speed.
Therefore, instead of just having a large block of memory, we do it in a whole sequence of memories that get bigger and bigger.
Register (Data Registers, Address Registers) -> Cache -> Main Memory -> Disk
Hack Computer
Hardware
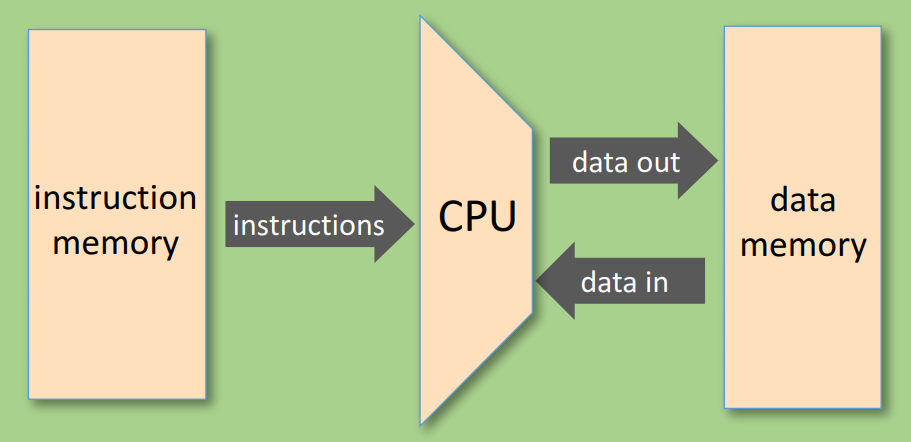
Say, this is a 16-bit computer:
- Data memory (RAM): a sequence of 16-bit registers
RAM[0], RAM[1], RAM[2],…
- Instruction memory (ROM, read-only): a sequence of 16-bit registers:
ROM[0], ROM[1], ROM[2],…
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): performs 16-bit instructions
- Buses: Instruction bus / data bus / address buses
Software
Hack program is sequence of instructions written by the Hack machine language.
Hack Machine Language:
- 16-bit A-instructions
- 16-bit C-instructions
How does the program run? (Control)
- The Hack program loads in the ROM;
resetbutton is pushed;- The program start running.
Registers
The Hack computer recognizes 3 registers:
- D: used to store data
- A: used to store data / address the memory
- M: represents the currently addressed memory register:
M = RAM[A]
The A-instruction Syntax
@value means (1) set the register to the value value; (2) select the register reg[value], or the M register above.
Example:
1 | # Set RAM[100] to -1 |
Because A is for “addressing”.
Binary Syntax
The number after ampersand “@” is a small non-negative number ($0 ~ 2^15 - 1$).
So, the “@” becomes a leading zero in Binary syntax.
1 | # @21 would be |
The C-instruction Syntax
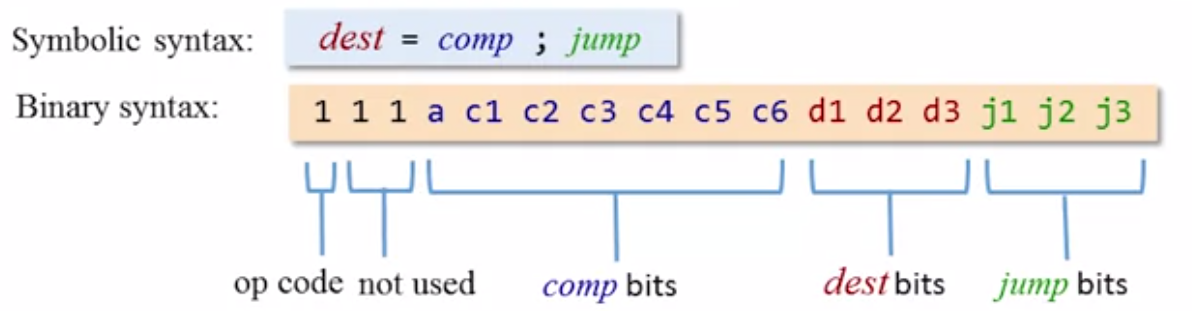
1 | dest = comp; jump |
![C-instruction Syntax]/images/Nand2Tetris/C-instruction%20Syntax.png)
Note:
- Compute the value of
comp, and store it intodest; jumprepresents comparing with zero;JMPmeans unconditional jump. A convention is do0; jmp, and this is an unconditional jump;- If the Boolean Expression (
comp jump 0) is true, then jump to execute the next instruction stored in RAM[A]; - Remember to “address” the register first.
Example:
1 | # Sets RAM[300] to the value of the D register plus 1 |
1 | # If (D-1 == 0) jumps to execute the instruction stored in ROM[56] |
Binary Syntax
The complete specification is: